European Robin
Erithacus rubecula
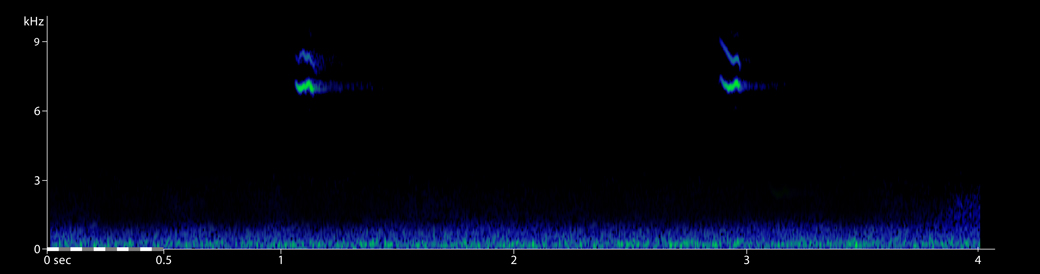
European Robin Erithacus rubecula Hanko, Uusimaa, Finland, 03:29, 28 September 2019. Flight calls of several nocturnal migrants; the first call is shown in high-resolution sonagram i) below. 190928.DF.032915.01 Please use headphones.
European Robins Erithacus rubecula never seem to be very far away. We enjoy watching them going about their business, but there is far more to this species than meets the eye. Listening to Robins migrating at night can be an exhilarating experience, and it usually coincides with the peak of autumn or spring migration.
Mysteriously, during the day they do not have any call that is particularly associated with flight. It seems reasonable not to expect them to have one at night either. However, attentive listeners have known the nocturnal flight call of the Robin for a very long time (eg, Lack 1954, Naumann 1822). If you listen carefully you may notice that in the daytime, apart from the ubiquitous tik call, Robins also give a shrill tsi rather frequently. It is this tsi that they adapt for use as a nocturnal flight call.
European Robin has just one type of flight call, which is rather variable. Any given individual seems limited to its own variant, so it is often possible to track each Robin as it crosses the sky (eg, listen to the individuals that stand out in recording f, g or k below).
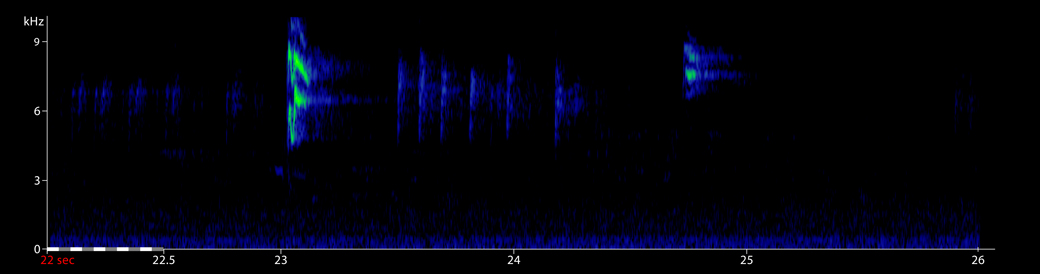
European Robin Erithacus rubecula Sagres, Vila do Bispo, Portugal, 07:10 21 October 2019 (GM). Tsi calls of perched migrants at dawn. The sonagram shows calls starting 22 seconds into the recording. 191021.MR.070710.02
Identification
tsi calls
- duration 67 – 117 ms (90% range; median 86 ms; n = 92)
- frequencies from 5.2 – 9.4 kHz (mean min 6.5 kHz ; mean max 8.4 kHz; n = 92)
- typically two parallel frequency bands, at their closest less than 1 kHz apart, often descending, or occasionally just one band (see example d); recordings of better quality may show additional faint band below and/or above (c)
- two main bands can be highly independent; the bands are often inflected to different degrees or in different directions (g, j); calls that are ‘level’ in both bands are rather uncommon
- bands often have at least one fairly sharp kink or angle (c, l), not sharp spikes rising out of a more level band (cf Spotted)
- lower band averages shorter (a, j), having a duration of 28 – 104 ms (90% range; median 78 ms; n = 87), though many calls have both bands the same length
- lacks fine modulations that would be capable of giving a buzzing quality, though shallow ones appear occasionally in the lower band (b)
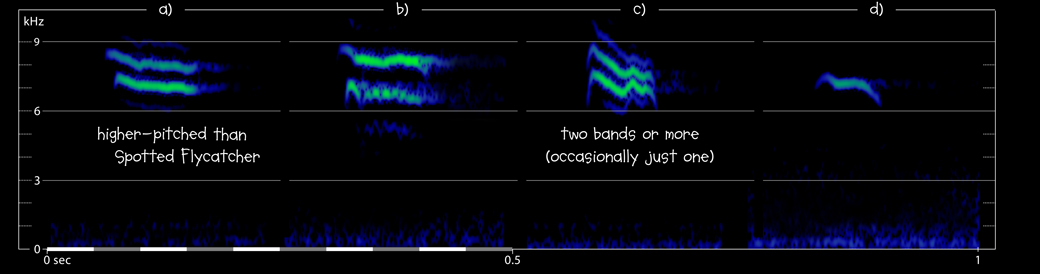
a) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Cabriz, Sintra, Portugal, 04:47, 30 October 2011. Flight calls of more than one nocturnal migrant; sonagram shows first call, after 1 sec. 111030.MR.044704.21
b) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Cabriz, Sintra, Portugal, 01:56, 29 October 2011. Single flight call of a nocturnal migrant at very close range. 111029.MR.015603.21
c) European Robin Erithacus rubella Sagres, Vila do Bispo, Portugal, 03:37, 3 October 2018 (GM). Single flight call of a nocturnal migrant. 181003.MR.033738.11
d) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Sagres, Vila do Bispo, Portugal, 01:16, 29 October 2017 (GM). Three flight calls of a nocturnal migrant, all with just a single band; first call shown. 171029.MR.011617.02
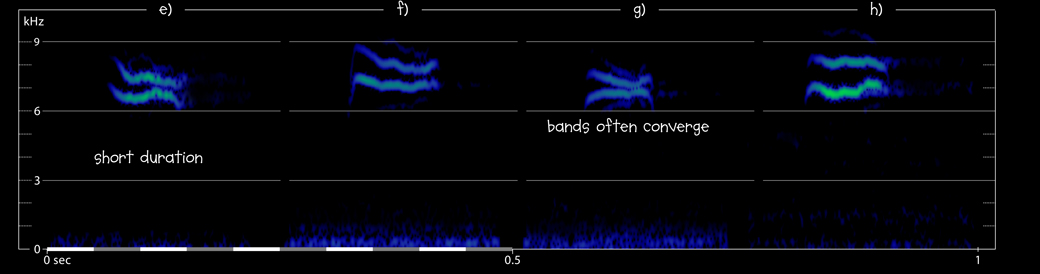
e) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Bialowieza Forest, Podlaskie, Poland, 00:22, 3 October 2012. Background: light rain. Call shown occurs after 16.6 sec. 121003.MR.002228.02
f) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Besh Barmag, Siazan, Azerbaijan, 06:09, 7 November 2018 (BB). Flight calls of at least three nocturnal migrant; sonagram from call at 20.8 sec. 181107.MR.060948.12
g) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Cabriz, Sintra, Portugal, 05:55, 17 October 2018. Flight calls of more than one nocturnal migrant, close to dawn; sonagram from call at 30.8 sec. 181017.MR.055536.02
h) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Martinhal, Vila do Bispo, 03:44, 4 October 2018 (GM). Flight calls of several nocturnal migrants; sonagram from call at 11.9 sec. 181004.MR.034407.01
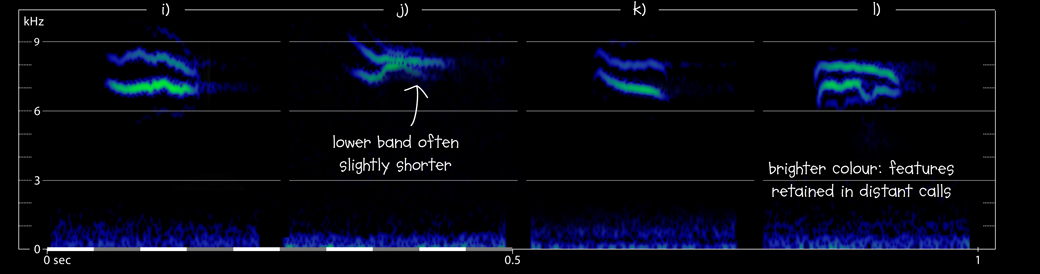
i) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Hanko, Uusimaa, Finland, 03:29, 28 September 2019. Flight calls of several nocturnal migrants; the first call is shown. 190928.DF.032915.01
j) European Robin Erithacus rubella Kirchmöser, Brandenburg, Germany, 02:38, 20 April 2019 (Lukas Pelikan). Flight call of a nocturnal migrant, very high pitched.
k) European Robin Erithacus rubella Kirchmöser, Brandenburg, Germany, 00:53, 15 October 2015 (Lukas Pelikan). Flight calls of several nocturnal migrants; the first call is shown. Note that you can distinguish at least two individuals by their consistent calls. One of them calls at 1 and 10.5 sec; the other at 6.5 and 13 sec.
l) European Robin Erithacus rubecula Potsdam, Brandenburg, Germany, 02:42, 12 September 2016 (Lukas Pelikan). Flight call of a nocturnal migrant.
Effects of recording quality
- Closer calls appear to have more than two bands, and may show a wider frequency range.
- Distant calls appear slightly shorter than they really are; fine details at upper and lower extremes of frequency disappear (darker blue features on sonagrams).
Similar NFCs
- Spotted Flycatcher Muscicapa striata has seep calls that average 13 ms longer and c 1 kHz lower-pitched. They have straighter lines showing only limited inflection over the call as a whole. A majority of Spotted NFCs have one or more sharp, upward-pointing spikes towards the end, lacking in Robin NFCs. Bands rarely differ noticeably in length. See also phenology.
- European Pied Flycatcher Ficedula hypoleuca has zzz calls that average almost twice as long, are lower-pitched and cover a wider frequency range. Pied has a buzzing quality caused by fine frequency modulations, which are strongest at the start of the call. Bands usually follow roughly the same inflection as one another.
- Hawfinch Coccothraustes coccothraustes NFCs are similarly high-pitched, have two or more bands and are only slightly longer than Robin calls, but have an instantly recognizable peaked shape, like a letter A without the crossbar.
Where and when?
- anywhere: over towns, forests, mountains, offshore
- strictly nocturnal: no known diurnal flight calls
- can be expected at any hour: a bias of activity towards second half of night
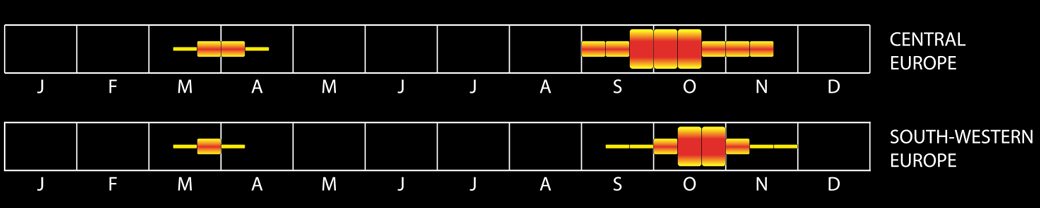
European Robin Erithacus rubecula Maximum estimates of calling individuals per night: low, medium and high activity. See introduction for a full explanation.
Note of caution
‘Nocmig’ can be a black art if ever there was one, and we all have to be open to the possibility that we are making errors on a grand scale. The point is to identify, acknowledge and learn from those errors, and gradually to become more accurate as time progresses. Until 2019, nocturnal counts from our listening stations in Portugal gave the impression that a significant number of Robins were passing in September, with some as early as August. The same pattern occurred in Germany with migrants apparent on the move as early as August. However, after some new insights it became clear that most of those early migrants were in fact Spotted Flycatchers.
While we are now much more confident about identifying nocturnal Robins, Spotted Flycatchers, European Pied Flycatchers and Bluethroats Luscinia svecica, it remains a disconcerting fact that for most of the common migrant chats and flycatchers Muscicapidae, we have never identified any flight calls at all. If species such as Common Nightingale Luscinia megarhynchos, Common Redstart Phoenicurus phoenicurus, Whinchat Saxicola rubetra or Northern Wheatear Oenanthe oenanthe do have NFCs, of a two-banded type similar to a Robin or a Pied or Spotted Flycatcher, then perhaps we are still misidentifying them as one or other of these species. Watch this space.
Towards dawn, it can become difficult to tell whether tsi calls are from birds in flight or perched in the bushes, both may use the same call. If a series of calls seems homogenous in volume and (in stereo recordings) direction, then the bird is surely perched. Normally, the start of tsi-calling from the bushes coincides with singing and tik-calling, which may be regarded as warning signs.
Further reading
Lack, D 1954. Call-notes, Erithacus and convergence. Ibis 96: 312-314.
Naumann, J F 1822. Naturgeschichte der Vögel Deutschlands. Volume 2. Leipzig.